
Estimation of measurement uncertainty in chemical analysis
9.2. Step 2 – Model equation
Model equation
http://www.uttv.ee/naita?id=17637
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N45YNwToyac
The model equation (equation 9.1) enables calculating the output quantity value (result value) from the input quantity values. Input quantities are the directly measured quantities (or are calculated from directly measured quantities). In addition, the model equation has to enable accounting for all important measurement uncertainty sources. In the case of this analysis the model equation is the following:
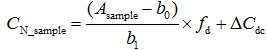 |
(9.1) |
The output quantity is CN_sample – ammonium ion concentration in the water sample.
The input quantities are:
Asample – absorbance of the dye solution obtained from the sample;
b1 and b0 – slope and intercept of the calibration graph;
fd – dilution factor;
ΔCdc – component taking into account uncertainty originating from possible decomposition or contamination.
The parameters Asample, b1, b0 and fd in the equation account for the directly measured input quantities. In contrast, ΔCdc is introduced only for taking into account uncertainty due to possible decomposition of the photometric complex and due to possible contamination. Its value is zero as will be seen in section 9.4, so, it does not contribute to the value of CN_sample. However, its uncertainty is different from zero and therefore will contribute to the uncertainty of CN_sample.


