
MOOC: Auditing Water Issues
3.1. Integrated water resources management
Meeting the increasing demand for water while avoiding excessive stress on water resources and water ecosystems is not an easy task. An all-encompassing approach to water management – integrated water resources management (IWRM) – has therefore become to be an internationally accepted concept to guide governments and private sector actors in making sustainable decisions on the use of water. The general idea is to manage different water-related aspects at the same time – political, economic, environmental and social.
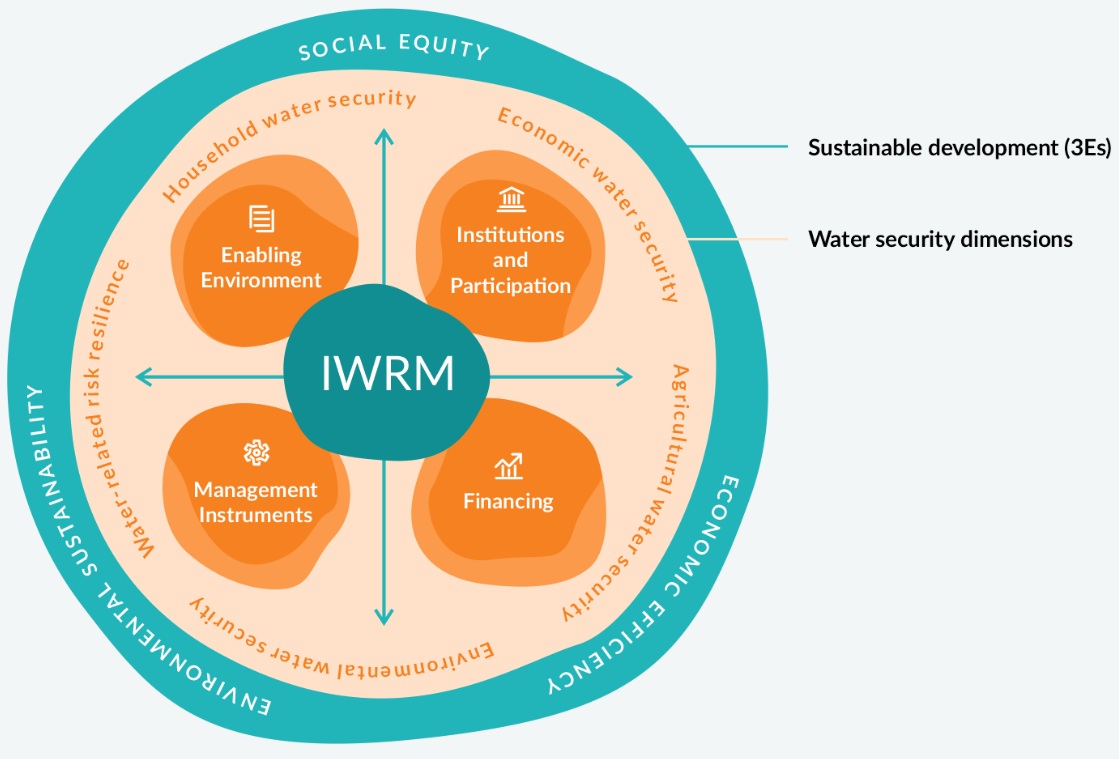
Figure 9. Aspects of IWRM contributing to the secure supply of water
Source: https://iwrmactionhub.org/about/iwrm-explained
The IRWM was at the centre of agenda at the Johannesburg World Summit on Sustainable Development in 2002 when it was stated as the necessary approach to be taken to achieve the safe drinking water Millennium Development Goal. Integrated river basin and watershed management strategies and water efficiency and plans were to be developed by 2005 for all major water bodies. More recently, the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals agenda has also firmly included the principles of IRWM, with its indicator 6.5.1 being the level of implementation of the IWRM, “Degree of integrated water resources management implementation”.
In this module, the River Basin Management Plan (RBMP) approach used in the European Union will be introduced. It must be noted that while the RBMP is in line with several principles of IRWM, it is distinct in being primarily oriented towards achieving environmental goals.


