Translon: a single term for translated regions
Świrski M. I, Baranov P et al.
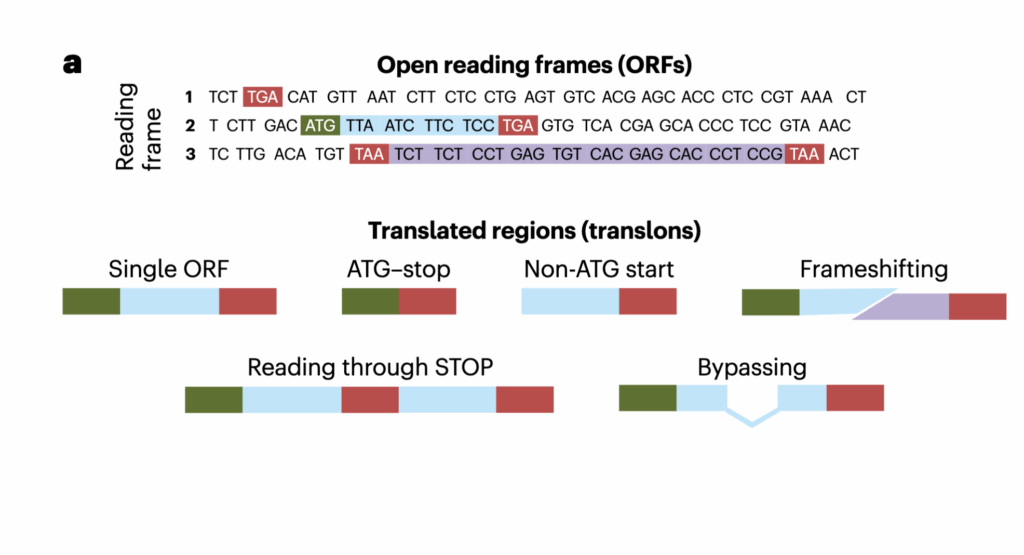
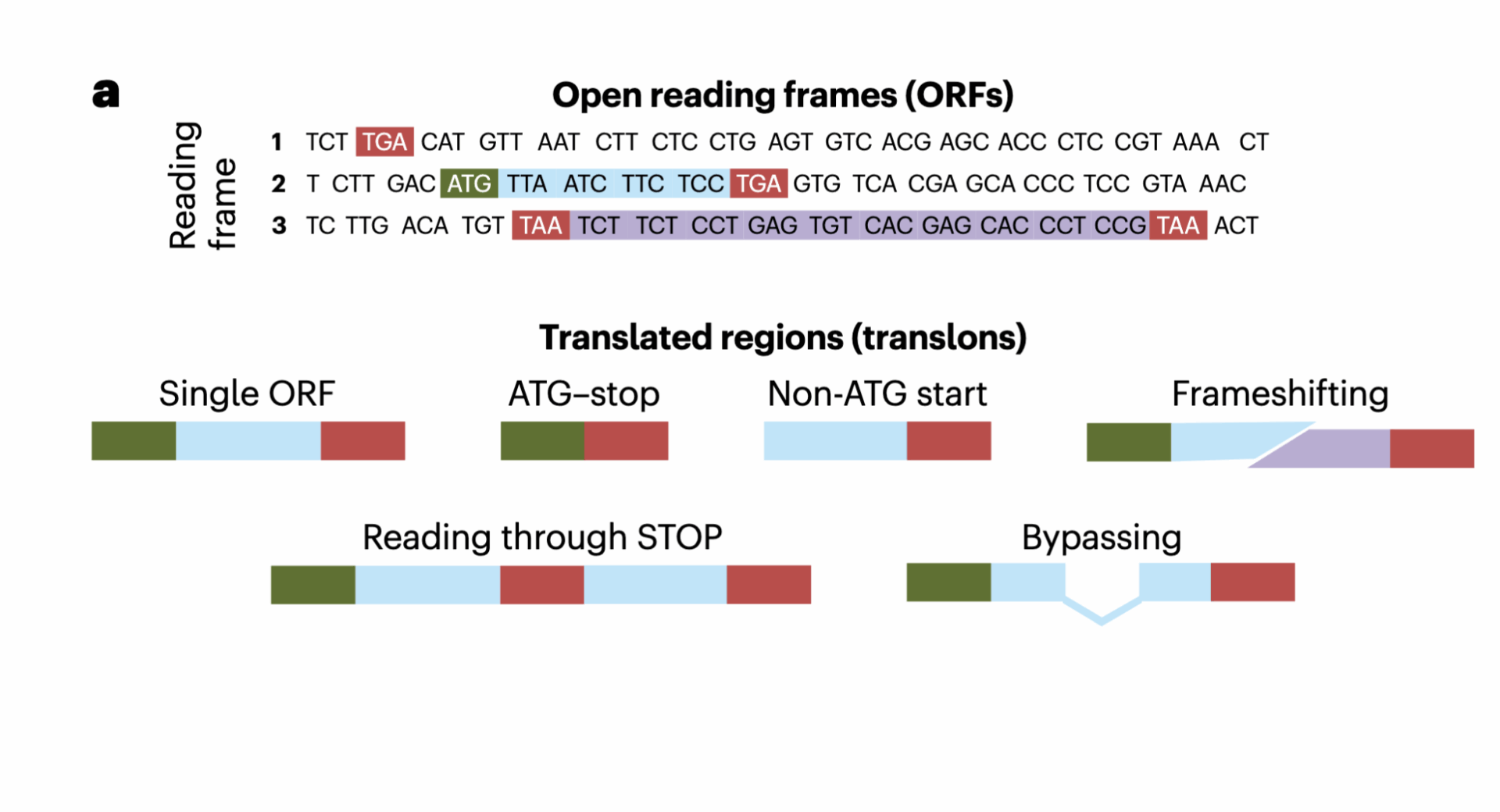
We suggest using the term ‘translon’ (short for ‘translated region’), which has previously been introduced but failed to gain traction. It aligns well with other terms describing gene structures: intron (‘intragenic region’) and exon (‘expressed region’). Translon would fill the gap in the vocabulary used to describe units of genetic information. Unlike the existing terminology, translon is defined directly, by the process it aims to capture, instead of indirectly, through sequence or function. Most ORFs are not translons because they are not translated. All CDSs are translons, but not all translons are ORFs. We expect that the term translon will reduce confusion when discussing translated regions and will facilitate development of more biologically realistic annotations.
Nat Methods. 2025 Oct;22(10):2002-2006. DOI: 10.1038/s41592-025-02810-3.