In Vitro Reassociation Assay to Measure the Formation of 80S Ribosomal Particles Using Salt-washed Ribosomal Subunits
Hallik A, Veeremaa A, Tamm T. In Vitro Reassociation Assay to Measure the Formation of 80S Ribosomal Particles Using Salt-washed Ribosomal Subunits. J Vis Exp. 2025 Dec 16;(226). doi: 10.3791/69529. PMID: 41490052.
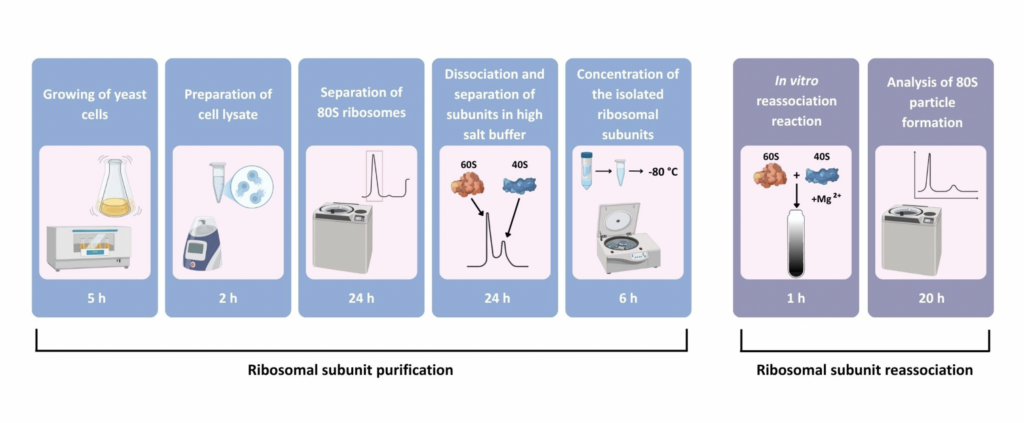
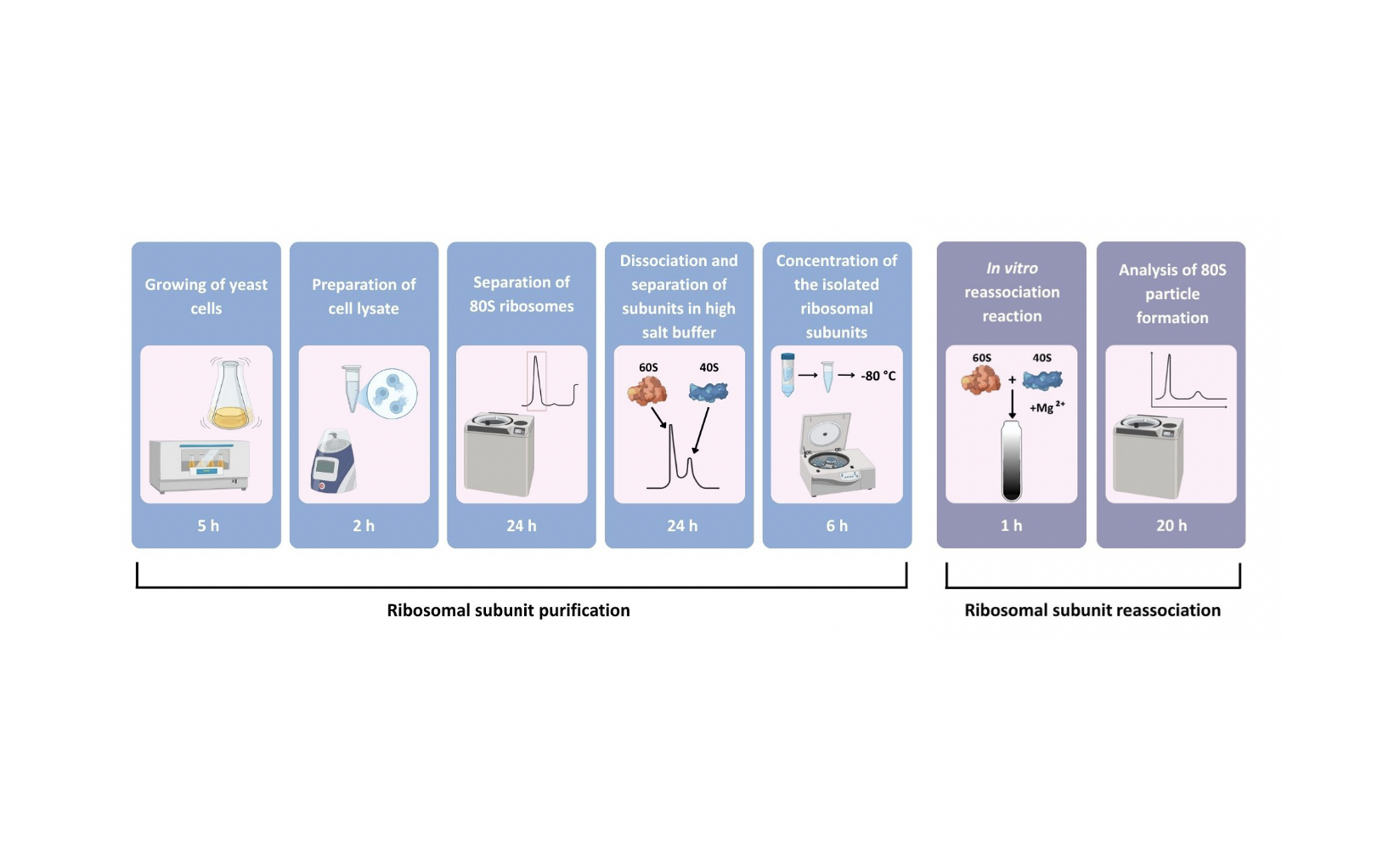
Ribosomes are molecular machines that are responsible for protein synthesis in all living cells. All ribosomes consist of two subunits. In eukaryotes, the 40S and 60S subunits interact during translation initiation to form the functional 80S ribosomal particles. These subunits are joined by contacts known as intersubunit bridges. To investigate how damage or mutations affect ribosome functionality, the in vitro reassociation of ribosomal subunits can be employed. In this method, eukaryotic ribosomes are first isolated, then the subunits are dissociated under high-salt condition using sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation. The purified, salt-washed ribosomal subunits can subsequently be reassociated at different magnesium concentrations to monitor the formation of 80S particles. As an example, the formation of 80S particles using the purified 60S subunits from a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain lacking the ribosomal protein eL24 is analyzed. Thus, this method enables the investigation of the structural integrity of the purified ribosomal subunits. Additionally, the method enables the evaluation of the roles of ribosomal proteins and rRNA in ribosomal subunit joining outside of the translational context.