
MOOC: Introduction to environmental auditing in the public sector
1.1. Sustainable development
Sustainable development
Environmental governance advocates sustainability as the supreme consideration in managing all human activities – political, social and economic. The concept of sustainability relies on sustainable development. Sustainable development can be explained in various ways, but the most widely recognised definition was phrased by the Brundtland Commission in 1987:
“Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
Sustainable development is based on the three pillars of sustainability: economic, environmental and social sustainability. It is only achieved when there is balance or a trade-off between these three aspects (see figure below).
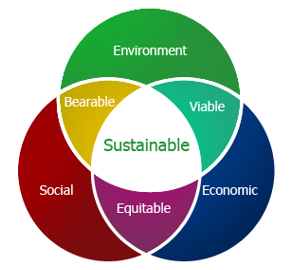
Source: http://macaulay.cuny.edu/eportfolios/akurry/files/2011/12/SDspheres.jpg (archived)
Some authors have expanded this approach and added a fourth pillar (for example cultural, political or institutional), but it is most important to understand that sustainable development is a holistic, integrated approach, meaning that in order to achieve sustainable development, there needs to be a balance between different spheres of life.
Sustainable Development Goals
At the United Nations Sustainable Development Summit in 2015, world leaders adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which includes a set of 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aimed at ending poverty, fighting inequality and injustice and tackling climate change by 2030. These 17 goals, listed below, are all accompanied by specific targets – 169 in total [Source: United Nations website on Sustainable Development Goals]

Sustainable development goals:
- End poverty in all its forms everywhere
- End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture
- Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
- Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
- Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
- Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all
- Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all
- Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
- Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation
- Reduce inequality within and among countries
- Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
- Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
- Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
- Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development
- Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss
- Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels
- Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development
 | Reading suggestion!See more details about the SDGs and targets at https://sdgs.un.org/goals Countries and the UN are regularly compiling reports on the implementation SDGs. See the United Nations Sustainable Development Report 2024. |
 | Thinking exerciseHas your country issued a SDG status report/ a UN voluntary national review? Have a look on your country’s profile on achieving the Sustainable Development Goals in 2024. What are the ‘red’ SDGs (“major challenges remain”) in your country? |
 | Reading suggestion!The UN Department of Social and Economic Affairs has issued Handbook for the preparation of voluntary national reviews. The 2022 edition. (2022) |
Sustainable development indicators
Sustainable development is a very complex and interconnected field. In order to know whether government is on a right track, it is necessary to measure the success or failure of achieving measures.
To measure the implementation of SDGs, a global indicator framework has been developed by the Inter-Agency and Expert Group on SDG Indicators (IAEG-SDGs). The global indicator framework was adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017. The list includes 231 indicators on which general agreement has been reached. [Source: UN Sustainable Development Goals indicators website]
 | Reading suggestion!Read more about the indicators on the UN webpage This handbook is targeted towards national statisticians to enable them to monitor the progress made in the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals based on data produced by national statistical systems. |
 |
Tip for an auditorThe concept, goals and indicators of sustainable development can be used for developing audit questions and audit criteria in all policy areas. See Modules 2-3. |
Sustainable development requires an effort from all sectors. As such, in an ideal situation, the evaluation of sustainable development achievements would be incorporated into all audits, not just environmental audits.
INTOSAI and Sustainable Development Goals
INTOSAI is an organisation uniting supreme audit institutions of public sector in most countries. The INTOSAI Strategic Plan 2023-2028 recognises SAIs’ contribution to the achievement of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development as one priority area.
 |
Reading suggestion!Special guidelines have been developed by INTOSAI (IDI) on how to audit SDGs: IDI SDGs Audit Model The reports on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) published by the INTOSAI member SAIs can be found in the INTOSAI Atlas on SDGs. |
 | Thinking exerciseBelow are five audit topics. Recall the list of 17 SDGs and think about them to decide, which SDGs would need to be considered when conducting these audits. You may also wish to think about the potential interlinkages between the SDGs. 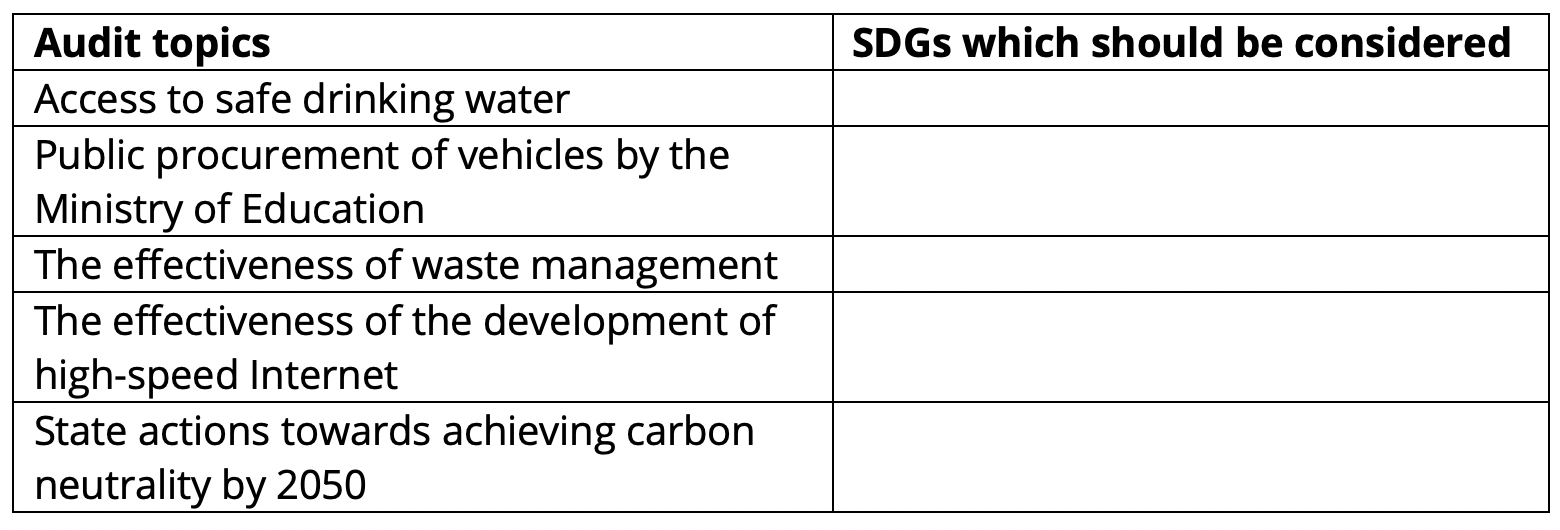 |
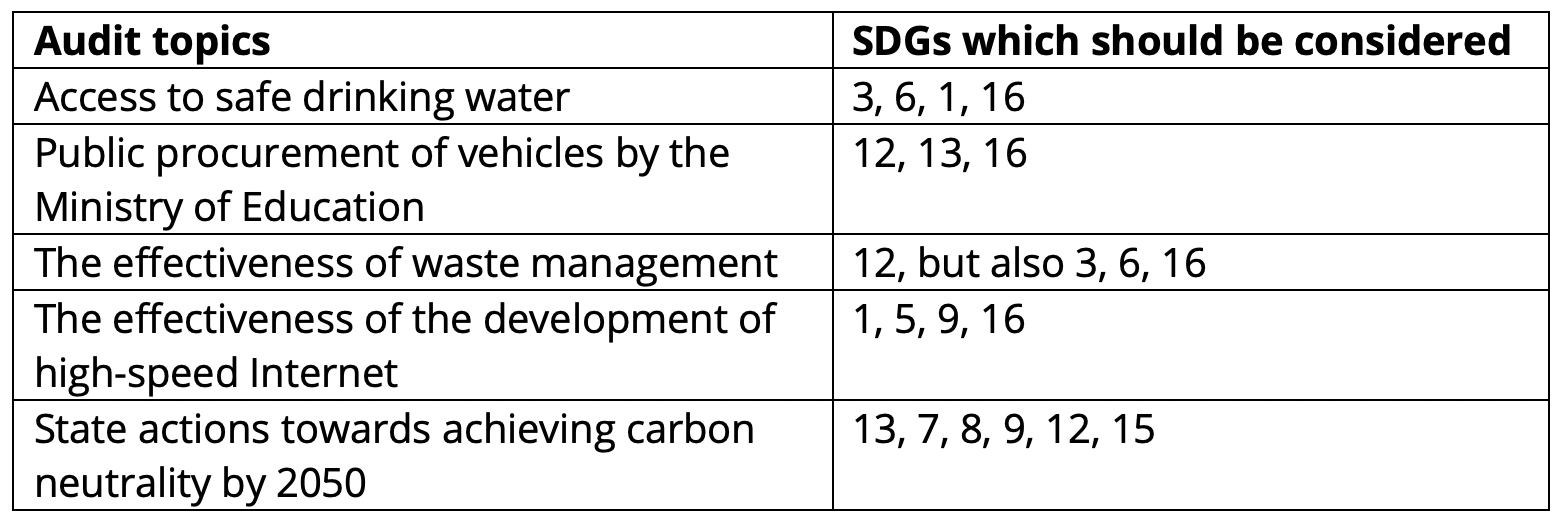
It must be kept in mind that there are many interlinkages, interactions, synergies and trade-offs between individual SDGs and their targets.


