Morphology of Nervous System
Ganglia
Ganglia are ovoid structures containing cell bodies of neurons and glial cells supported by connective tissue. Ganglia function like relay stations – one nerve enters and an other exits. The structure of ganglia is illustrated by the example of the spinal ganglion.
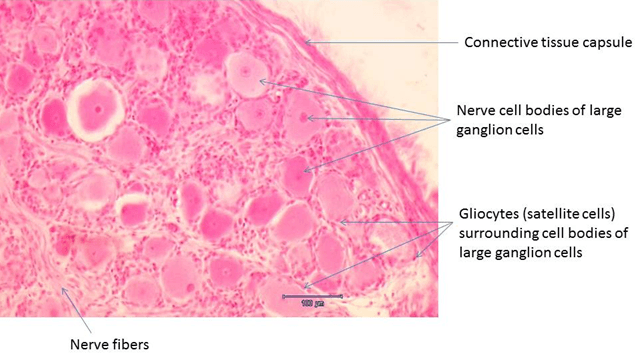
The spinal ganglion with large ganglion cells (pseudounipolar neurons) is located in the dorsal root of the spinal nerve. In the centre of ganglion cell is a nucleus with prominent nucleolus. The round cell body of ganglion cell is surrounded by the layer of small supportive glial cells – gliocytes of the ganglion (gliocyti ganglionici, also known as satellite cells). The ganglion is surrounded by the connective tissue capsule.


