
MOOC: Auditing the Sustainability of Infrastructure
1.3. Sustainability of Infrastructure
According to the OECD, sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The paper brings out the three main factors of sustainable development: environmental, social and economic factors.
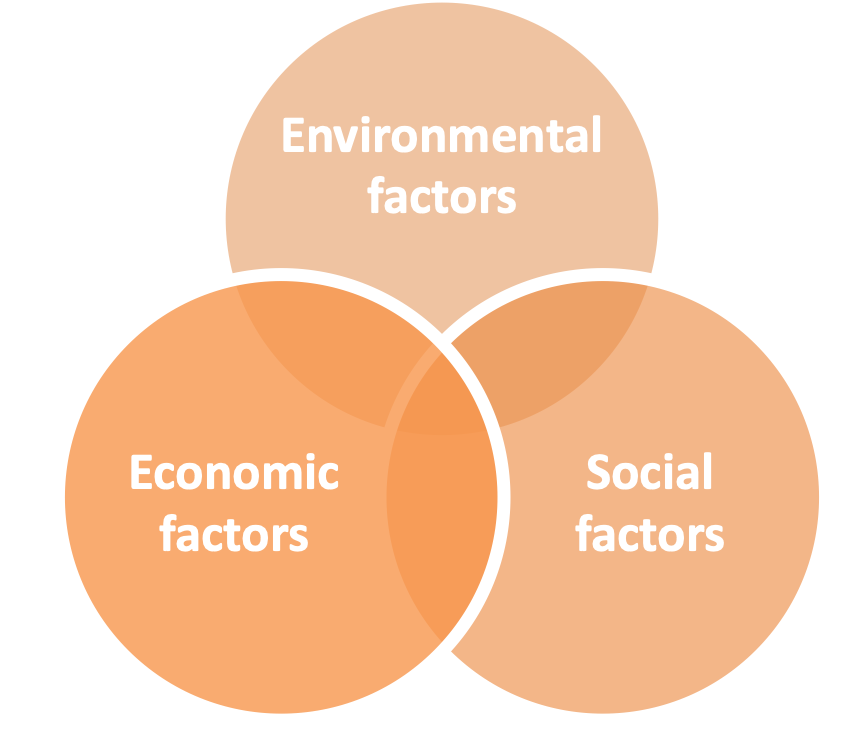 Sustainable development recognises the need for a balance between economic, social and environmental factors. In other words, our decisions should take into consideration the potential impact on society, the environment and the economy, while keeping in mind that our actions affect the future. The latter is important to remember, as, for example, it might seem reasonable to cut down a forest to gain immediate economic and social benefits, but if this action leads to the depletion of a forest, the overall result may be a substantial loss in income, biodiversity, capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, etc.
Sustainable development recognises the need for a balance between economic, social and environmental factors. In other words, our decisions should take into consideration the potential impact on society, the environment and the economy, while keeping in mind that our actions affect the future. The latter is important to remember, as, for example, it might seem reasonable to cut down a forest to gain immediate economic and social benefits, but if this action leads to the depletion of a forest, the overall result may be a substantial loss in income, biodiversity, capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, etc.
The three pillars of sustainable development – people, habitats and economic systems – are inter-related. We may ignore their interdependence for a few years, but people and the economy depend on ecosystems and the services they provide. Therefore, sustainability is not the same as environmental friendliness but is a more complex concept. Sustainable development requires effort from all sectors.
Economic, social and environmental impacts should be determined in the planning phase, i.e. the project start up stage of infrastructure development. Generally, environmental impact is examined in an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) and socio-economic impact is determined in the cost-benefit analysis, which should also take into consideration the environmental impact determined in the EIA. Find out more about these studies in the next module.
We will now take a closer look at each of the three pillars of factors of sustainable development, according to the OECD publication.


