
MOOC: Auditing the Sustainability of Infrastructure
2.4. Operational Service
The operations of an infrastructure object must adhere to the law and to the conditions set during the planning phase. For example, in most countries, there are limits on the permitted levels of contamination of water, air and soil as well as for waste management. Most countries have also developed systems for monitoring environmental impact. On top of that, the closure and decommissioning of infrastructure should be regulated by law. Further on in the course, an audit example on this topic will be presented.
In this stage, the maintenance of infrastructure also takes place. As mentioned in the lifecycle costing section, maintenance and repairs can make up quite an extensive part of the costs of an infrastructure project.
Audit example:
‘Operation and maintenance of public roads – considerably more expensive than agreed’ (Swedish National Audit Office, 2019)
The Swedish National Audit Office audited the operation and maintenance of public roads and found that the deviations between the procured price and the final cost are large for the basic contracts investigated. The average contract increased by 41 per cent. The following table brings out the questions and criteria used in the audit and brings out the main conclusions of the audit, illustrating the main reason for the cost increase.

 | Audit suggestion!For another example of auditing the cost of maintenance works, take a look at this audit by the Netherlands Court of Audit, which looks at maintenance of the main water system. Besides auditing the cost of maintenance, auditors can also look at the planning and supervision by the state. Take a look at this audit by the Supreme Audit Office of the Czech Republic, which, among other things, examines how the repair works and maintenance of bridges are planned and monitored by the state. |
Environmental Management Systems
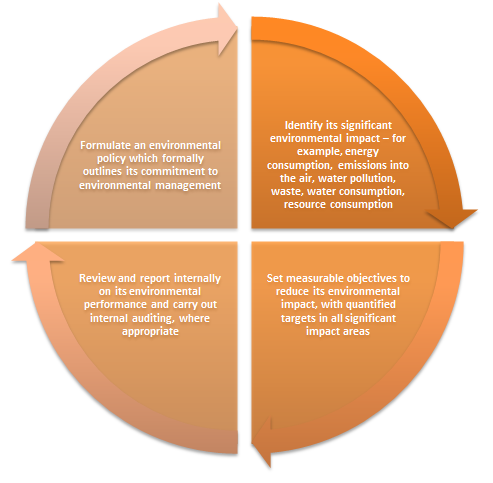
An infrastructure operator may implement an Environmental Management System (EMS) to monitor, improve and control the infrastructure object’s environmental performance. The International Organisation for Standardisation has developed a set of standards that provide practical tools for companies and organisations in managing their environmental responsibilities. This internationally accepted standard series for implementing an effective EMS is known as ISO 14000. The ISO 14001 standard in particular sets out the criteria for an EMS and can be certified.
To obtain ISO recognition for its EMS, an organisation must:
More information on Environmental Management Systems can be found here:
Besides the economic costs and revenue of this stage and the environmental impacts, modern infrastructure companies can also have a social dimension. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a self-regulating business model that helps a company be socially accountable—to itself, its stakeholders and the public. By practicing corporate social responsibility, companies can be conscious of the kind of impact they are having on all aspects of society, including economic, social and environmental impact. To engage in CSR means that, in the ordinary course of business, a company is operating in ways which enhance positive perception of the incfrastructure development by the society, and environmental sustainability instead of contributing negatively to them.
Another corporate self-regulation widely spread nowadays is environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria or ESG Governance. It is usually a score compiled from data related to intangible assets within the enterprise. It could encompass assets such as diversity, human and animal rights, responisble investment strategies, employee compensation, waste management, etc.
 |
Reading suggestion!Read more about CSR on Investopedia. Read more about ESG on Investopedia. |
 |
Thinking exercise:Can you think of some companies in your country that practice social responsibility? What activities do they undertake? |
Furthermore, this is the stage is which disposal and decommissioning of infrastructure takes place. It is important that both adhere to the rules and regulations in place and the conditions set in the contracts. For example, auditors can check whether the environment of the infrastructure site is restored accordingly or whether all the requirements for disposal are followed correctly and by the entity that was assigned the duty.


